7th March 2025
Someone, somewhere, wrote your coursebook. They don’t know you, they’ve never met your students, and they might not even be familiar with your country. This means the content of your coursebook wasn’t made specifically for your class. It's more like a store-bought suit - close enough, but not a perfect fit. It probably needs a few tweaks. In this post, we’ll look at how AI can help you make those adjustments.
Why Use AI to Adapt Your Coursebook?
Imagine for a moment that you are the richest teacher in the world. You might hire someone to rewrite your coursebook specifically for your students. You’d tell them what your students struggle with and ask for solutions. If you wanted to pre-teach vocabulary before a reading, they’d create a plan. If half your class found a text too hard, they’d simplify it. If your students need to practice for a test, they’d change the questions in the coursebook to match.
Here’s the thing: with AI, you can do all these things for free. In this post, I’ll show you how. We’ll go through everything from pre-reading and vocabulary to grammar and comprehension, all while making your coursebook as relevant as possible for your students.
Before we get started…
A couple of quick notes. Firstly, the screenshots in this post come from ChatGPT, Gemini, or Qwen. These AI tools can ‘read’ images. To adapt your coursebook, take a photo or screenshot of the page and paste it into your chat with one of these AI text generators. Secondly, the prompts in this post are aimed at adapting your coursebook content. They can also be used to adapt texts and questions from other sources.
Before Reading
Prediction
Reading lessons don’t usually start with reading. Before diving into a text, it’s helpful to get students talking or thinking about the topic. This way, they can bring up any relevant ideas or language, making it easier to connect with the material in the coursebook.
The prompt below generates some prereading activities that can help your students get in the right mindset before reading.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. Suggest some prediction activities that students can engage in before reading the text. These should aim to get students thinking about the topic, activate schemata and get them curious about the content of the text. The students are aged {age} and at {CEFR} level. Text: {add the reading here}.
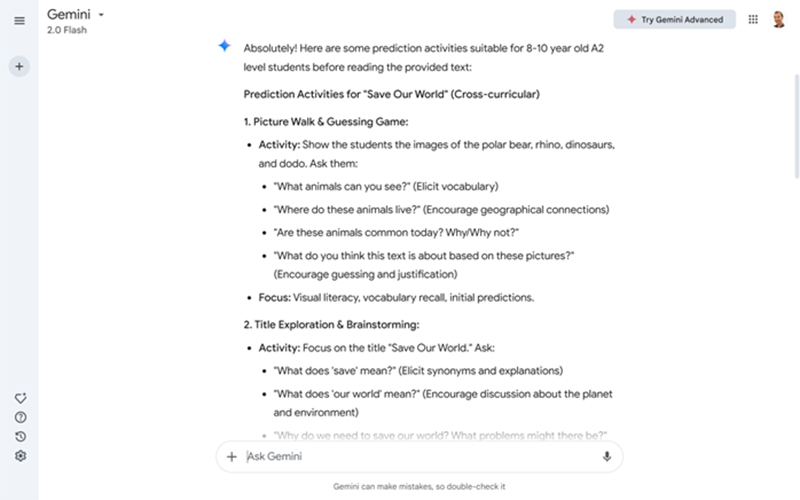
Simplifying Texts
One of the biggest hurdles with reading lessons is that the passage your students are meant to read is too difficult for the students to understand. If your students can’t understand the reading, the rest of the lesson will be an uphill struggle. You could explain the text line by line, but this would be as fun as exciting as watching grass grow. You could give the students a simpler passage, but then your learners would miss all the comprehension questions in the coursebook. Not ideal either. AI offers another possibility.
AI can create a new, simplified reading passage for your students which matches any reading comprehension questions in your coursebook. You could let the class read the simplified reading, then do the coursebook exercises. You could even give different students different passages depending on their level, keeping everyone challenged.
The prompt below will create a simpler version of your coursebook text, while making sure that students can still answer the same comprehension questions with either version.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook along with its associated comprehension questions. Your task is to rewrite the text by simplifying both the grammar and vocabulary while ensuring that all essential information remains intact. The simplified version should still allow for accurate answers to the original comprehension questions.
After rewriting the text, conduct a 'think through' analysis. This involves comparing the answers derived from both the original and simplified versions of the text to confirm that they align perfectly. Ensure that the simplification process has not altered the meaning or the ability to answer the comprehension questions correctly.
Text and questions: {reading passage and reading comprehension questions}
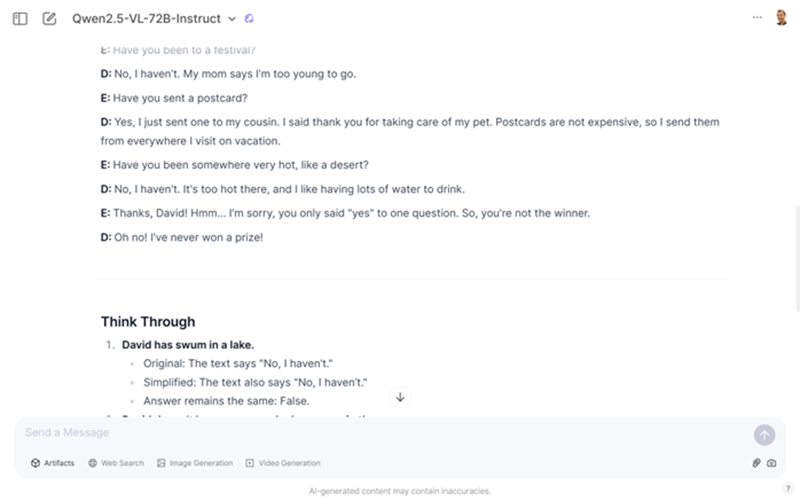
Localising Texts
We mentioned earlier that the person who wrote your coursebook has probably never been to the country where you teach. That means your coursebook is unlikely to include examples that are especially relevant to your students. To solve this, AI can rewrite your coursebook texts, adding local examples that your students can relate to.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook along with its associated comprehension questions. Your task is to {delete as appropriate: add to the text/rewrite the text/replace parts of the text} to make this more relatable to students in my location, which is {your country or region}. After the text is contextually adjusted, check that it aligns with the comprehension questions. Text and questions: {add the reading passage and comprehension questions here}.
Difficult Vocabulary
Open a coursebook, find a reading passage, and it should include quite a few words your students don’t know. Coursebook writers include these to introduce new vocabulary in context. This can help students understand how new words and phrases are used. However, unknown or new words can lead to frustration. If students don’t get the vocabulary, they might not understand the text. Let’s look at how AI can help.
Pre-Teaching
Pre-teaching is one way to handle this. It involves teaching difficult words before students read a text. This helps them feel prepared, so they’re not stuck trying to figure out words while reading. You can use simple definitions, synonyms, examples, or even translations. The goal is to make sure your students understand enough of the words to make sense of the text. The prompt below will find words that your students might find difficult and suggest ways of explaining these to the class before they read.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. Find some difficult words that require pre-teaching. What do they mean? How can I explain them to my students before they read? For each word give (1) a simpler English synonym (if one exists) and (2) a translation into {your first language}
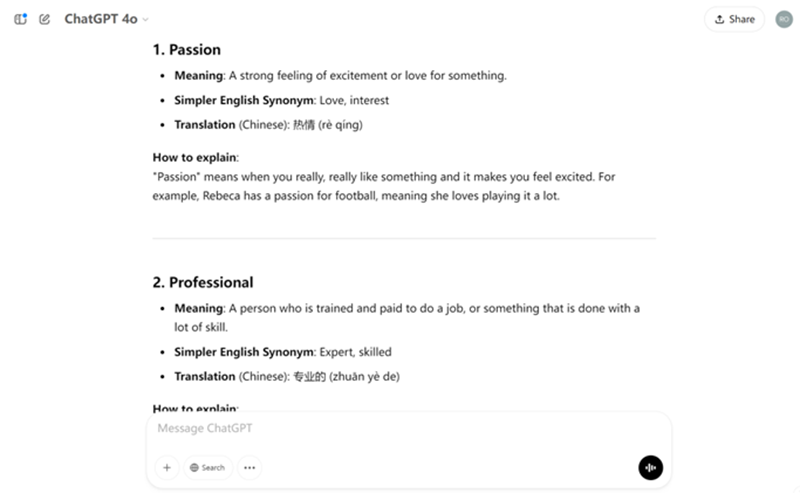
Guessing From Context
Pre-teaching has its limits. If students never come across words they don’t know, they will be unprepared when they read something "real" outside your class. The solution to this is guessing from context. But this is easier said than done, especially if your students haven’t practiced this skill before.
AI can help you guide your students to guess the meaning of difficult words in a text. It can spot less common vocabulary and create questions that you can use to lead students to discover the meanings on their own. Pick and choose the questions you think would work best with your class.
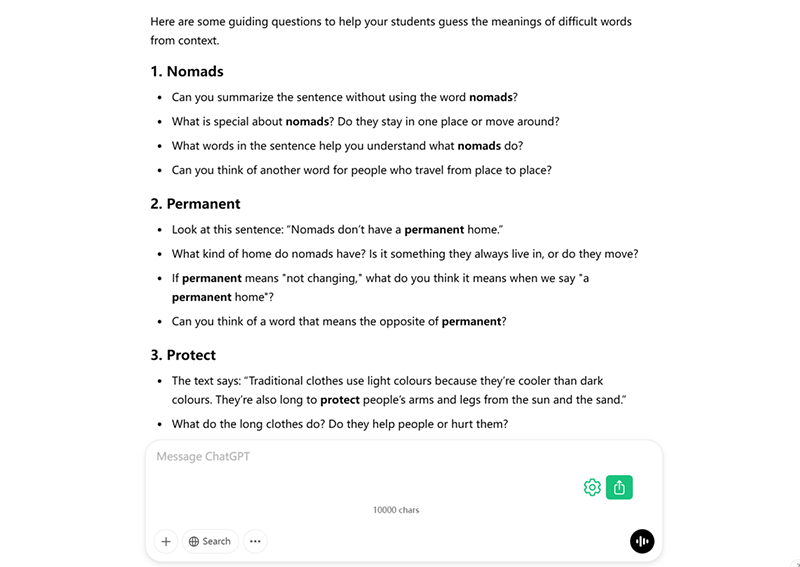
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. Find some difficult words or chunks of language (like phrasal verbs, idiomatic expressions, collocations, formulaic expressions, or fixed phrases) that my students are unlikely to know. I want my students to guess these words from context. Can you give me some questions (in simple English!) to guide them to guessing the meaning of these words? Include questions that guide students to do some of the following (but only if appropriate):
- summarise the sentence without using the unknown word.
- Identify the part of speech
- look for words in the surrounding sentence that give clues about the meaning.
- suggest students replace the word with another word
- look at the word structure (affixes, similar looking words in English or another language)
Adding Explanations
Another way to deal with difficult vocabulary is by adding explanations. This lets students keep reading instead of running into a wall when they see an unfamiliar word. The prompt below will create three longer versions of your coursebook text, adding either first language translations or English explanations for challenging words. You can change the percentages to control how many words get expanded upon. Students can better understand any blocking vocabulary by reading the explanation or translation.
Prompt: Rewrite the following text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. Identify some challenging words or phrases that students might find difficult, ensuring these make up 5-10% of the total words in the text. Create three distinct versions of the text, keeping most of the original text intact and only adding explanations or translations as needed:
- Version 1: Include a translation into {your students’ first language} in brackets immediately after each difficult word.
- Version 2: Provide an explanation of the word or a simpler synonym in English, either as part of a relative clause or in brackets after the word.
- Version 3: Add a word bank at the end of the passage for students to refer to while reading.
Do not remove any words from the original text.

Grammar
Predicting Challenges
Often, it’s not the words in a text that make it hard to understand, but the grammar. AI can analyse the grammar in a text and find structures that might be tricky for your students. The prompt below will help you predict potential challenges your students might face while reading and suggest ways to help them overcome these.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. I want you to analyse the grammar in the text. Highlight areas that my students might find difficult to understand. List these starting with the hardest to understand. Then, suggest ways of helping students understand the grammar in these parts. Coursebook text: {enter the coursebook text here}.
Grammar Focus
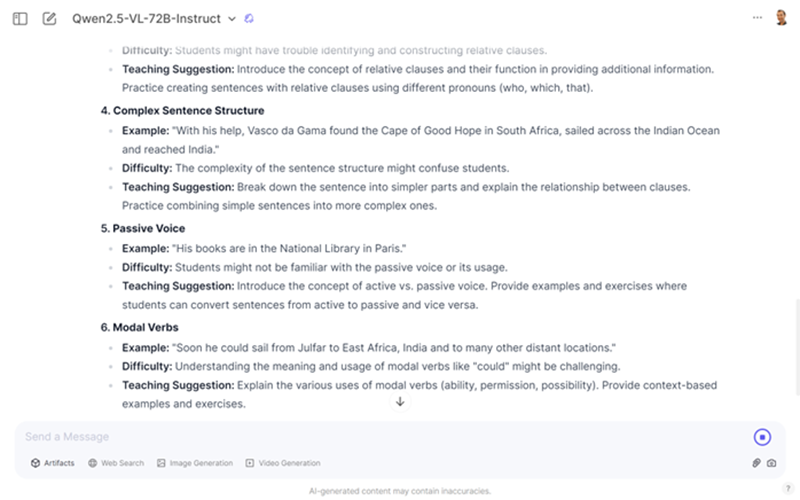
After reading the text, you might want your students to focus on the grammar in the passage. One of the most common coursebook complaints I hear from teachers is “There’s not enough grammar!” If that’s an issue with your coursebook, use the prompt below to create grammar exercises based on the more complex grammar in the text. The AI will decide which grammar point to focus on, but if you have a specific grammar point in mind, edit the prompt.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. Create a grammar exercise based on this text to help students practice the more difficult grammar points from the reading. The exercise should include at least three different types of activities, such as:
- Sentence transformation (e.g., changing direct speech to reported speech)
- Gap-fill exercises (e.g., filling in the correct prepositions or verb forms)
- Sentence building (e.g., constructing sentences with given words)
- Identifying grammar structures (e.g., finding examples of specific tenses or conditionals)
- Creative writing (e.g., using specific grammar points to write about the passage or their own experiences)
Each activity should include:
- Simple instructions for students, using language that’s easier than the reading itself.
- An example to show how to complete the activity.
- Suggested answers at the end of the exercise.
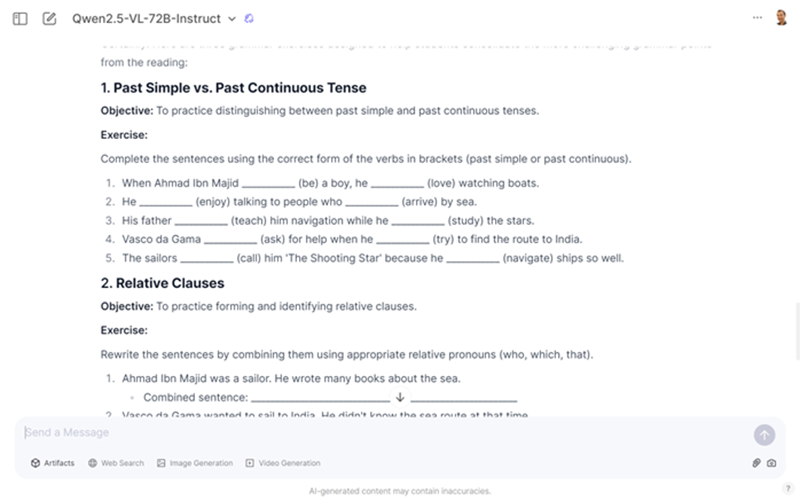
These prompts work just as well with grammar in an authentic text, such as a news article, blog post, or short story. The prompt above generates several grammar-focused activities, allowing you to choose the one that’s most suitable for your class.
Reading Comprehension
Summarising
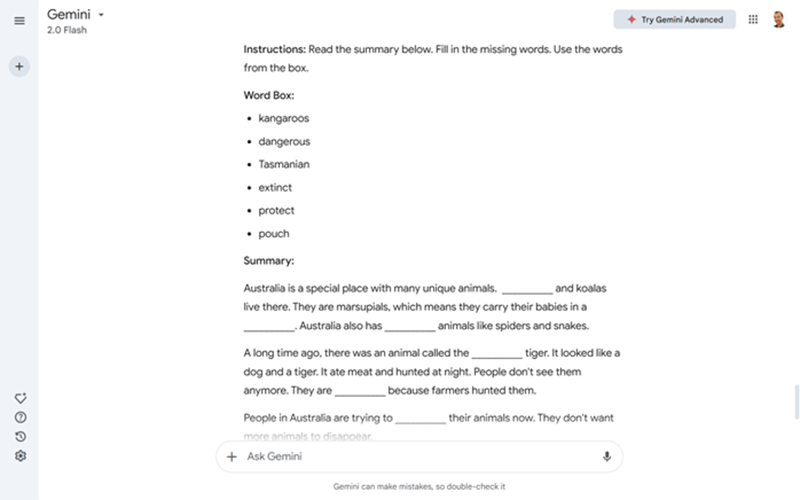
Another issue with global coursebooks is they often don’t match local tests. Teachers who want to focus on exam preparation might need to carve out time from each class to practice past paper questions. A more efficient alternative is to change the coursebook questions so they match the test. Imagine that your students need to prepare for a test with a gap-fill summary of a reading passage. AI can create this kind of question while matching the coursebook text, as in the prompt below. This lets your students practice for the test while making sure you cover what’s in the book, killing two mosquitos in one swat.
Prompt: I will show you a text from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. I want you to go through the following steps. (1) Analyse the Text Level: Evaluate the text's grammatical complexity, sentence length, and vocabulary. (2) Create a Lower-Level Summary: Write a brief summary of the text using simpler language. (3) Develop a Gap-Fill Exercise: Transform the summary into a gap-fill activity by removing key words. Students will fill in the gaps to demonstrate their reading comprehension. Add instructions for students.
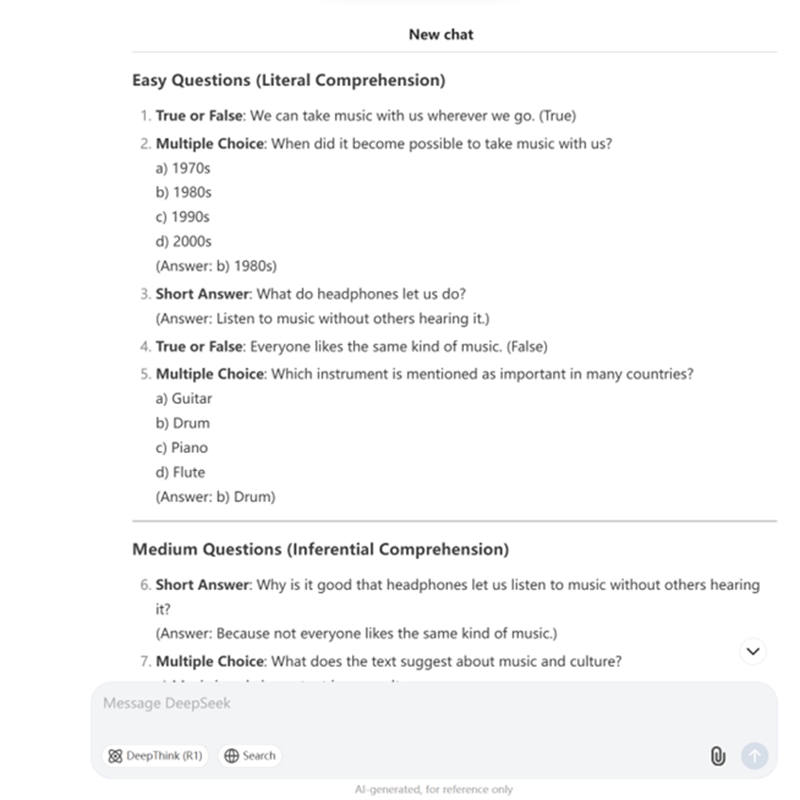
Generating Comprehension Questions
Checking reading comprehension isn’t always straightforward. The questions in your coursebook might be too easy, too difficult, or there might not be enough of them. Whatever the reason, AI can help you create additional questions. You can edit the bullet points in the prompt below to customise the questions for your students' needs.
Prompt: I have a reading passage for my students from an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) coursebook. I need you to create a set of reading comprehension questions at different difficulty levels. The purpose of the questions is to assess students' understanding of the passage.
1. Question Types: Include a variety of question types, such as:
- True/False
- Multiple Choice
- Short Answer
- Personal Discussion Questions
2. Difficulty Levels:
- For easier questions, use wording similar to the text to check literal comprehension.
- For harder questions, paraphrase or require inferential or critical thinking.
3. Personal Discussion: Add a few open-ended questions that encourage students to connect the text to their own experiences or opinions.
4. Text: The passage I will provide is: {Insert the text from your coursebook here}
Words of Caution
At the start of this post, I mentioned that the person who wrote your coursebook has never met your students. That’s true. But keep in mind that ChatGPT, Gemini, and Qwen haven’t either. Be sure to check whatever they produce — it might be wrong.
Much of what we’ve covered in this post might already be in the teacher’s notes that come with most coursebooks. If you have them, read them. They include insights from the author, suggestions for adjusting activities, and ideas on how to use your coursebook effectively. While AI can do these, the results won’t be as reliable as those from the author.
Let’s get into some specifics. While AI can predict vocabulary that may be difficult for your students, these insights shouldn’t replace your own experience. Similarly, the prediction activities might not always match your students' level or interests, so use them with care. Review any AI generated questions before giving them to your students. You might find that the questions don’t match the text. They might be too difficult. Generative AI is great at a lot of things, but writing for lower-level learners isn’t one of its strengths—at least not yet. It’s a good idea to run them through a vocabulary checker to make sure the language matches the level you’ve set.
Lastly, avoid relying too heavily on AI. It can be a helpful tool, but it can’t replace your own judgment and experience. Treat it like the richest teacher in the world would treat a coursebook author hired to adapt a coursebook for a specific class. Let AI do the hard work of writing and editing, but use your knowledge of your students to decide what to use.
Conclusions
Even with the limitations we've discussed, AI can save you hours when adapting coursebook content. It’s like having your own coursebook editor, on hand 24/7, ready and willing to adjust reading passages, generate custom questions, and predict where students may struggle. This lets you focus your energy where it's needed most—on student interaction and engagement.
While this post has concentrated on reading sections, the strategies we’ve discussed can be applied to various areas of your coursebook. Whether it’s simplifying vocabulary, creating extension activities, or adapting grammar exercises, AI can make your teaching more efficient.



