19th July 2024
Test prep can be daunting. Students come to us with minimal time and maximum expectations. They might want to focus on the test, even when they really need to focus on improving their English. Teachers are supposed to know everything about question types, strategies, and grading criteria, all while keeping students engaged and motivated. It’s an almost impossible job. In this blog post we’re going to look at how AI can help lift some of the burden. We’ll start by looking at why AI can be especially useful for test prep. Then we’ll consider how to use AI to help students prepare for listening, speaking, reading and writing questions. We’ll round things off by looking at some of the limitations of using AI in this area.
Why Use AI for Test Prep?
- Efficiency. Teachers can save valuable time by letting AI handle repetitive tasks like generating practice exercises and grading students’ answers. This frees you up to focus on more individualised instruction.
- Appropriacy. AI produced materials can be more appropriate than authentic test questions. For some students, authentic questions can be overwhelming. AI can help create questions that can help learners get used to the format of a test without being too difficult.
- The Nature of Tests. AI is increasingly being used in high-stakes English tests, both in writing test questions and even evaluating answers (like in the Duolingo English test). By familiarizing students with AI-generated content, teachers can prepare them for the challenges they might encounter on actual tests.
- Instant Feedback. AI text generators can provide immediate feedback on students' work. This can help students identify their mistakes and learn from them quickly. Although your comments on students’ work might be better, AI’s is faster. This makes AI feedback the perfect out-of-class supplement for your in-class correction.
- Quality Sample Answers. AI can generate examples of high-scoring answers. These models can provide students with structure, vocabulary, and effective writing techniques. By comparing their own answers with these models, students can ‘steal’ good ideas to improve their writing or speaking.
Listening
Creating Listening Questions
Most high-stakes English tests ask test takers to listen to something, then answer comprehension questions. There are a few reasons why you might need to create your own listening questions, such as:
- The authentic questions are too hard.
- You don’t have enough authentic questions.
- You want to expose students to wider variety of accents than those in the authentic questions.
- You need to create your own test.
There are a few advantages of using AI to create these instead of recording yourself. AI can give students practice listening to different accents and unfamiliar voices. You can also change the speed of the audio. This lets learners get used to listening to connected speech at lower speeds. Slowing things down can make connected speech features easier to hear and give students more cognitive space to understand what’s going on.
To use AI to create your own listening test questions you’ll need a script. Then you’ll need to turn the script into audio. Finally, you will need to write comprehension questions to go with the audio.
Creating a Listening Transcript
To create an audio script, you’ll need an example. Some tests might provide transcripts. If yours doesn’t, you can use a speech-to-text AI (like Turboscribe) to generate a transcript. Upload an audio file and a few sections later the speech-to-text AI will create a transcript.
Next show your transcript to an AI text generator. Ask it to analyze the transcript and create a new text in the same style but on a different topic. The example below was created by using a transcript from the Pearson Test of English.
Prompt: I will show you a transcript from the listening section of a high-stakes English test. I want you to analyze this for length, complexity, etc. Then create a new transcript in the same style but on a different topic. Listening transcript: ### [listening transcript]
You may want to check the text is at a similar difficulty level to the original by using a readability check (like Hemmingway app). If the readability score is much higher or lower than the original, ask AI to make it simpler (or more complex).

From Transcript to Audio
Next, open a text-to-speech AI (like TTS maker). Copy and paste the new listening transcript, then choose a voice. Choose ‘More Settings’ to change the length of pauses and the rate of speech. Then click ‘Convert to Speech’ and download the mp3 file.
Creating Listening Questions (and Answers)
Last but not least, you’ll need questions to go with the audio. In the example above (from the Pearson Test of English), test takers need to summarise what they hear. Both the Pearson Test of English and the Duolingo English Test ask students to write a summary after listening. AI can create a sample answer by summarizing a transcript of the audio. For example:
Prompt: Write a minimum of 50 words but no more than 70 words to summarise the following text: ### [text]
Students can compare their own summaries with the AI summary and look for:
- Important points they may have missed
- Useful phrases used by the AI
- How the sample is organised (compared with their own)
That covers how to create an answer. Next lets’ look at how to generate new listening comprehension questions. To do this you’ll need:
- the transcript of your new audio
- a transcript of the original audio you’ve based this on
- the comprehension questions which go with the original transcript.
Prompt: Read this transcript and the comprehension questions which go with it. Transcript: ### [original transcript] ### Comprehension questions: ### [original comprehension questions] ### Now create a new set of comprehension questions in the same style as those above which match this text: ### [transcript of your new audio]
Reading
Creating Reading Texts and Questions
It goes without saying that a lot of test prep involves answering practice test questions. Depending on the test and how long your students have to prepare, you might need to create your own questions. For some exams and question types this is easy. For others, like reading, it’s hard. AI can help. Many AI text-generators are good at taking a sample and extrapolating from this to create new samples.
Let’s take IELTS reading as an example. Say we’ve run out of IELTS reading passages or want to give our learners a passage that they’re unfamiliar with. AI can create a reading text for us.
Start by giving AI an authentic exam question. Ask AI to analyze the style, tone and complexity of the writing. Then create a new text with the same style, tone and complexity.
Prompt: Look at the text from a high stakes English test. Analyze the style, tone and complexity of the text, then create a new text of a similar length in the same style, tone and complexity as the original.
This gets you the reading, but not the questions. To make the questions, you’ll want an example and a text. Give these to AI and use a prompt (like the one below) to create new questions.
Prompt: Look at the first text and questions. Then create similar questions which match the second text. First text and questions: ### [text and questions]. ### Second text: ###.
Alternatively, you could try creating both the questions and the text all at once…
Prompt: Look at the first text and questions. Then create a new text in the same style and questions which match the new text in the same style as the first set of questions. First text and questions: ### [text and questions].

Creating Simplified Reading Texts
Some question types are more complicated than others. Many questions require specialist training to be able to answer. Real test questions are great for practice. But less proficient students might need practice with simpler examples before tackling authentic questions. AI can analyze existing questions and create equivalents for simpler reading passages. Once your students understand how the questions work, they can move on to more authentic practice. To get started, take a reading text and questions. Ask AI to make a simpler version of the passage. Check the reading level of the new text to confirm that this is simpler than the original passage.
Prompt: Please simplify the text to a grade [number] reading level, but keep the questions in the same format: ### [text and questions]
Explaining Answers to Reading Questions
Most reading and listening questions come with solutions. But sometimes the solutions aren’t enough. More important than knowing the right answer is knowing why it’s right. Teachers can help in this area, but only in class. AI can help when students are practicing at home. Students can check any answers that they get wrong or are confused about. The following prompt can generate answers and explanations to reading questions.
Prompt: Read the passage and answer the questions. For each answer explain why this is correct and why other answers are wrong. ### Passage: [reading passage] ### Questions: [questions].
However, AI sometimes gets questions wrong. If you (or your students) already have the answers, ask AI to explain the reasons.
Prompt: Read the passage, the questions and the answers the questions from a high-stake English language test. For each answer explain why this is the correct answer. ### Passage: [reading passage] ### Questions: [questions]. ### Correct answers:
Speaking
Practicing for Speaking ‘Interviews’
The big problem with practicing for speaking tests is that they usually require someone to roleplay being the examiner. That’s fine in one-to-one classes, but what do you do if you teach a class of 30? Give each student a two-minute interview in a one-hour class? Or ask the students to wait weeks until you have time to give them a mock test? You could ask students to interview each other, but this is far from realistic practice. Now there is a new option. Use AI.
For spoken interviews, ask a text-to-text AI (like Chat GPT or Gemini) to roleplay being an examiner while your students roleplay being the test taker. This involves a few steps. Firstly, if you want your students to actually practice speaking, they’ll need to enable audio as input. A few AIs allow this, including ChatGPT, Gemini, etc. Getting this up and running is the first step.
Next, you’ll need a prompt. For a test like IELTS, some text-to-text AI might be able to approximate the experience of talking to an examiner. However, this often takes a bit of trial and error. You might find the AI making mistakes like asking multiple questions at once or commenting too much or too little on the students’ answer. Your first prompt is unlikely to hit the bullseye. Tweak your prompts to tell the AI to do more of some things and less of others.
An alternative is to ask the AI to roleplay being a test-prep teacher, rather than an examiner, giving comments after each answer. This can allow students to get more feedback and means that the roleplay doesn’t have to be particularly authentic.
Another option is to use a GPT someone else has made for this purpose. For example, trying going to chatgpt.com/gpts, search for “IELTS speaking” and check out the options.
Mimicking Speaking Test Transcripts
For less common tests, an example often works better than a description. If you can find a transcript from a test (for example, from YouTube), you can use this to train an AI on how to roleplay being an examiner for a particular test. Ask the AI to read the transcript and note how the examiner interacts with the student and what questions they ask. Then you can ask the AI to role play being an examiner, while your students practice being a test taker.
Following the conversation, you’ll want to ask the AI for some feedback on your speaking performance. You can do this by:
- Asking for feedback on overall performance.
- Giving AI the grading criteria for the test and asking it to give feedback on these areas. Remember that AI won’t (at the time of writing at least) be able to give feedback on pronunciation or (to a slightly lesser extent) your fluency. It can however comment on, coherence, cohesion, content, discourse, grammar and vocabulary.
- Ask the AI to focus on one specific descriptor and get feedback on this area. Then repeat for another area.
- Ask the AI about ideas that the student felt they were unable to express clearly as they spoke. They could simply ask the AI to translate some words or phrases from their first language.
Sample Answers
It’s sometimes useful for students to see a ‘model’ answer. This is true both for speaking and writing. Before we jump into creating model answers for speaking, let’s look at how these (speaking or writing) can be used in class.
- Students can listen to (or read) the sample answer and discover how useful phrases (like discourse markers) get used.
- After writing a draft, students analyze a sample answer and decide what they can ‘steal’ to improve their own writing.
- Learners can read a sample answer and grade it. The class can then discuss the grades and comments. This can help students better understand the grading criteria.
- Students can use multiple AIs to create sample answers to the same questions, then choose their favorite and say why.
Remember that it can be as (or possibly more) useful to listen to authentic samples of test takers answering questions (especially for speaking). However, AI answers can be valuable if you want to create an answer to a specific question or if you’re looking for an answer in a specific accent. If you do decide to go ahead and create some AI answers to speaking questions, you’ll need an exam question, an AI text generator and a text-to-speech AI (like TTS Maker).
Start by giving an AI text generator the question and generate a script.
Prompt: Pretend that you are an IELTS band 9 test taker and give an answer to the following question: Question: ### [question]. ### Please use language appropriate for spoken discourse, avoid writing in too high a register and include contractions where appropriate. Use a maximum of [number] words.
Then go from text to audio by putting this into an AI text generator (like TTSmaker). (Remember that this type of answer will only be appropriate for long form speaking answers and not discussions with an examiner.)
Read Aloud Practice
Some tests (like the Duolingo English Test and Pearson Test of English) ask students to read a statement out loud or repeat something they’ve just heard. The test then analyzes for accuracy. Speech-to-text AI (like Otter.ai) can provide perfect practice for this by transcribing something that students read aloud.
To practice, you’ll need something for students to read. You could use authentic exam questions. For more focused practice, create short texts which include sounds that your students find it difficult to pronounce accurately.
Then, ask students to open a speech-to-text AI and read the short passage aloud. After reading, the students compare what the AI transcribed with what they read. Any differences indicate a mistake. Students note these, then try again, focusing on improving their performance.
Writing
Feedback on Writing Answers
A big part of improving your writing is getting feedback. In a previous post, we looked at how students can use AI to generate feedback on their writing. Most language tests have specific criteria that are used for grading writing. For example, on IELTS Writing, these are task achievement / response, coherence and cohesion, lexical resource, and grammatical range and accuracy. AI can organise feedback using these criteria, making it more relevant to the test.
Take a sample of your students’ writing, the question and the grading criteria and use the following prompt.
Prompt: Give this student feedback on their writing. This is an answer to a question on a high-stakes English test. Divide your feedback into the following areas: ### [test grading criteria]. ### Question ### [the question]. ### Students’ answer: [writing].
Sample Writing Answers for Essays
As discussed in the speaking section, students and teachers alike find sample answers to questions useful. The process for creating and using these is similar to that for speaking questions (above).
Sample Writing Answers for Descriptions
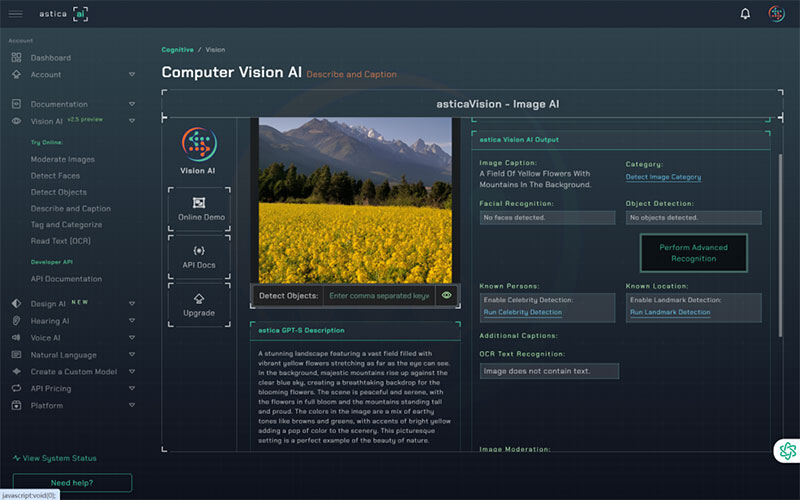
Some tests (like the Cambridge PET and the Duolingo English Test and) ask students to describe images. AI can now create sample answers for these questions. To create a description of an image, go to a ‘vision’ (or image-to-text) AI (like astica), upload a photo and generate a description. This can be used in the same way as the model writing and speaking answers discussed earlier.
Limitations
Although AI can be a useful tool for test preparation, there are some limitations to consider.
- Quality of AI voices (listening): Some AI voices may sound unnatural. Listening to unnatural voices is unlikely to be useful speaking practice for your students. Be careful to check the voices when creating audio files. Choose accents and speaking speeds on the AI text-to-speech generators which match those that students are likely to hear on the text.
- Monologues not Dialogues (listening): While creating monologues is easy using AI, creating dialogues is not (yet). If your listening test includes listening to multiple speakers talking to each other, you’ll need audio editing software. This which is more complicated and time-consuming compared with making your own monologues.
- Inaccuracies in answers (reading): AI may not always provide correct answers to questions. This could lead to confusion or even worse, students coming to the wrong conclusions about answers.
- Incorrect explanations (reading): Similarly, AI may provide incorrect explanations for why a particular answer is correct. This is less likely than incorrect answers, but could also lead to confusion. Using more than one AI model and comparing the comments makes this less likely.
- Text complexity (reading and listening): AI generated reading (or listening) texts may be more complex than those in authentic test questions. Check the reading difficultly level of any AI generated texts using a readability checker (like Hemingwayapp) and tweak the level of the text as required.
- Inaccurate question generation (reading): When creating new questions, AI may sometimes make up information. Read and check any questions before giving these to your students.
- Inauthentic interviews (speaking): Your AI examiner might go off script when practicing for a speaking test. Keep an eye on these speaking test role plays and make sure that students get the opportunity to watch real examples of speaking tests as well as doing mock tests with you.
- Limited feedback (speaking and writing): While AI can provide feedback on certain aspects of speaking and writing, it may miss important positives or negatives that a human teacher would catch. Avoid relying completely on AI generated feedback and use this as a supplement to your own.
Conclusions
AI offers some exciting possibilities for test preparation in English language teaching. AI can help teachers create practice materials and generate sample answers. AI can also help students by providing instant feedback and explaining answers to questions. However, it's crucial to remember that AI is a tool. It is not a replacement for experienced teachers or authentic test materials. By combining AI's capabilities with effective teaching, more students can get more help preparing for tests which have an outsized influence on the education and future careers.



