3rd November 2023
As a language teacher, one of the most important things you do is plan. It is difficult to overstate how important planning is for teachers. Most of what goes right and wrong in a lesson is down to planning. Planning is also one of the most time-consuming activities for teachers. If you’re anything like me, you probably spend as much (or more) time planning as you do teaching.
But some kinds of planning are more useful than others. Some institutions expect their teachers to write detailed plans for every class. These plans have to be submitted in advance and checked for quality control purposes. These plans aren’t likely to help you teach better classes. But they are likely to help you keep your job.
In this blog post, I’ll show you:
- how to write a lesson aim using AI.
- how you can use AI to help you plan lessons.
- how to use AI to generate ideas for activities.
- how AI can turn your rough ideas into a comprehensive plan.
- the limitations of using AI in lesson planning.
Let’s get started.
Writing Lesson Aims
Lesson planning starts, or is meant to start, with an aim. An aim is where you want your students to go. It needs to be specific and measurable, so you can tell if you’ve achieved it (or not). It should balance being aligned with the curriculum and being personalized for your learners. And it must be short enough that it makes sense to you, and any administrator that might read it.
AI can help you write aims for your lessons in two or three ways.
One way is to give the AI information about your class. That includes information about students, the topic, the target language, language skills and more. The AI can use this information to create an aim. In doing so, AI is replicating the process that teachers go through when writing an aim before writing a detailed plan. You might use a prompt like this:
Please give me suggestions for a lesson aim. My students are [level] and [age]. We are studying a unit on [language focus or topic]. They enjoy [add some of your students’ preferences]. Please begin the aim with “By the end of the lesson, students will be better able to”.

Above is an example of output from Bard.
In reality, planning doesn’t always start with an aim. I often start the planning process by thinking of one or two activities and build a plan around those. The last thing I write is the aim.
Another way of asking AI to write an aim is to show the AI your plan and ask it to create an aim based on the plan.

Above is an example of output from Bard.
AI can also help you check aims you’ve already written (or that an AI has written for you). Good aims usually follow a few important principles, like:
- Being measurable and specific.
- Focusing on what students will be able to do (not what they will learn).
- Includes examples of the target language.
- Starting with “By the end of the lesson, students will be better able to…”
You can ask an AI to check that your aims meet these standards. If they don’t, the AI can suggest changes.
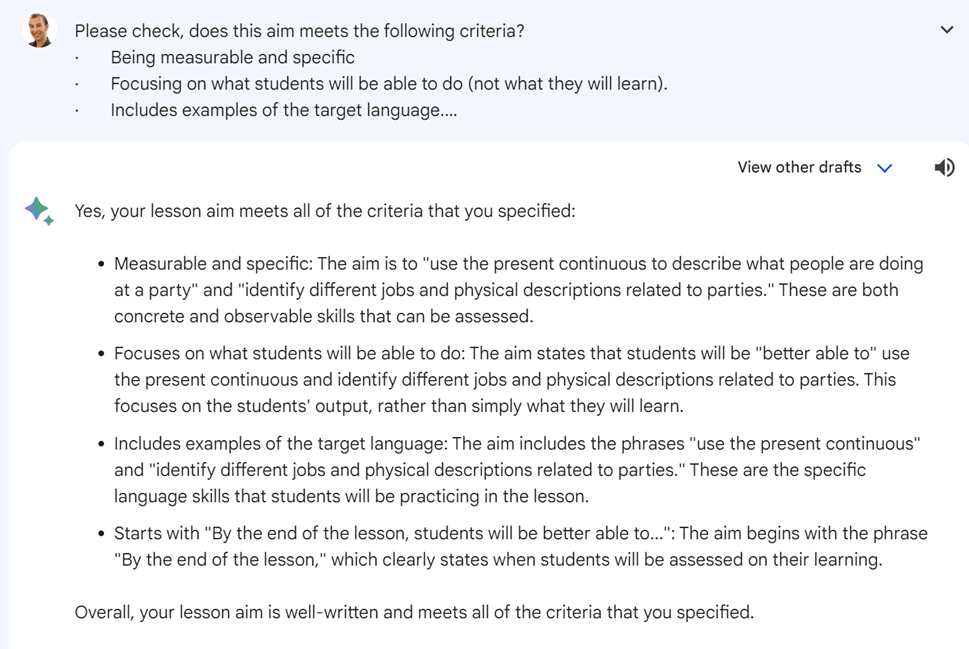
Above is an example of output from Bard.
Remember, you do not have to use the AI aim ‘as is.’ You can, and should, edit based on your own needs. Afterall, you’re the one who is going to have to teach the lesson, so make sure you’re happy with the aim.
Writing Lesson Plans
Now that we have an aim, we can turn to writing a plan. Again, there are several ways of getting AI to plan a lesson. We can:
- Give information to the AI and ask it to create a plan based on this.
- Give the AI the lesson aims and ask it to suggest activities.
- Show the AI previous lesson plans that you’ve made. Then ask it to create a new plan using the old plans as a template.
Key information
Let’s start by looking at what information the AI needs to create a useful lesson plan. You could include:
- The lesson aim. This is obvious, but on its own it’s not enough.
- A language focus. That’s the grammar, vocabulary, or pronunciation that you want your students to learn during the lesson. You may want to say more about this than you have already said in the aim.
- Language skills and sub-skills. Do you want your students to practice listening, speaking, reading or writing? Are there any strategies you want to teach your students that would help them develop these skills?
- The level of the students. You can describe this using the CEFR.
- Student preferences. What do your students enjoy doing in class? Surveys? Discussions? Competitive games? Also tell the AI about anything that your students don’t like doing (such as singing songs, spelling tests or craft activities)
- The context. This could relate to culture. For example, where are your students from and where the lesson is taking place? The AI can help take account of L1 issues, customs, and cultural norms. You can also tell the AI why the students are learning English. Are they planning on passing the KET in the next six months? Or are they looking to work in an English-speaking country as nurses?
- Timing. How long does the lesson last? Is there a break? Is there a maximum time you want the activities to last?
- Staging model. You can ask the AI to try to stage the activities as PPP (Presentation, Practice, Production), ESA (Engage, Study, Activate), TTT (Test, Teach, Test), CAPE (Context, Analysis, Practice, evaluation) or TBL (Task-Based Learning).
You might structure your prompt like this:
Please help me write a TEFL lesson plan.
- Lesson aim: By the end of the lesson, students should be better able to [lesson aim].
- Language focus: [vocabulary, / grammar / pronunciation and/or skills]
- Student preferences: [description]
- Students Age: [age range]. Level: [English level]
- Context: [language learning context]
- Staging model: [ESA / PPP / TBL]
Please output in a table format. Include enough content to last [the length of your class].
That might look like a lot of information. However, these prompts will not change much from one class to another. It will serve as a template for future use.
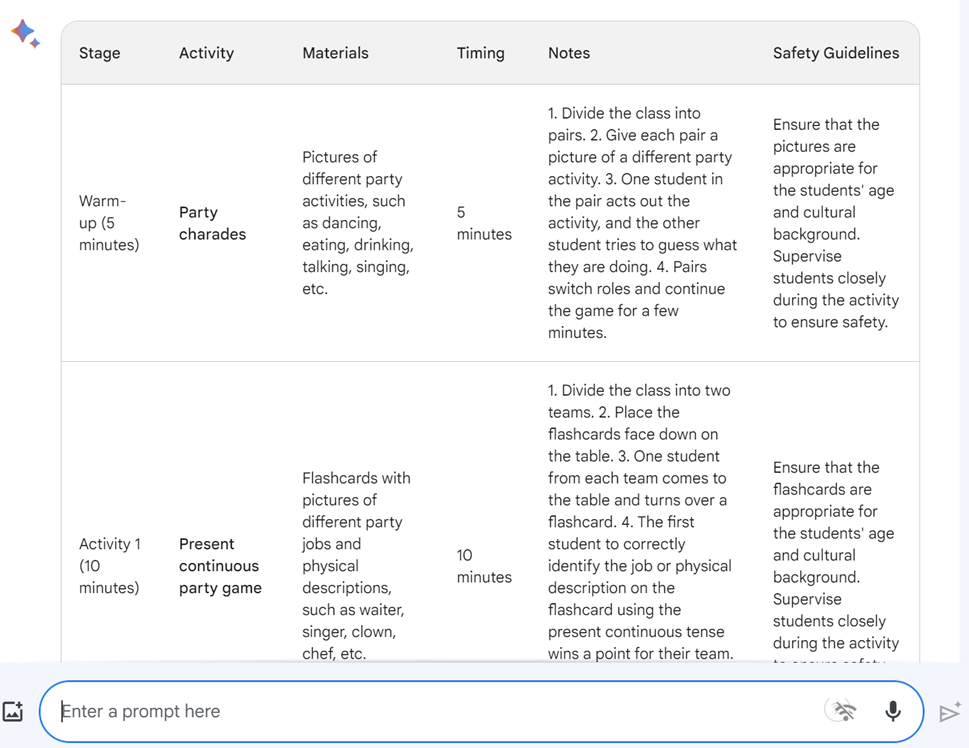
Above is an example of the output from Bard.
Activity suggestions
You can also ask an AI model to suggest activities for your lesson. Perhaps you’ve already gone through the process of planning and have a few gaps in your plan. AI can help fill these. I think of this as the AI equivalent of turning to the teacher next to you in the staffroom and asking, “Do you know any good activities for practicing the present perfect?”
Use a similar prompt as the one above to generate suggestions for activities. For example:
I want you to suggest at least five activities for a TEFL class. These should all be [presentation / practice / production] activities to practice [language point]. These activities should be appropriate for [level] [age] students in [context].

Above is an example of the output from ChatGPT.
Mimicking Your Style
You can also ask an AI to create a customized lesson plan, based on your previous plans. To do this, you need to show the AI an example of what an appropriate plan looks like. The AI will use this to understand your lesson planning (and teaching) style.
Start by copying and pasting a plan into an AI model. This will be your template. Next, ask the AI to analyze the lesson plan and say what it would need from you to create a plan like this.
Here is the prompt for this:
Here is an example lesson plan:
### [Example lesson plan] ###
What should I ask for you to produce a plan like this, using the same variables, and with the same style, tone of voice, methodology, and type of activities?
Take the answer and add it to your prompt from the previous section.
Please help me write a TEFL lesson plan.
- Lesson aim: By the end of the lesson, students should be better able to [lesson aim].
- Language focus: [vocabulary, / grammar / pronunciation and/or skills]
- Student preferences: [description]
- Students Age: [age range]. Level: [English level]
- Context: [language learning context]
- Staging model: [ESA / PPP / TBL]
Please output in a table format. Include enough activities to last [less length].
Please use the following style: [style from prompt]
Input the variables as before but ask it to use the same style and variables as the previous plan as in the example below. Then look at the reply.
Writing Up a Lesson Plan
As I mentioned earlier, some plans are written for teachers to use. Other plans are written for administrators to check. The plans I use when I teach nowadays are just a list of activities, some vocabulary, and a few notes. I know what the plan means, but I doubt it would make sense to anybody else.
AI can turn these notes into a formal lesson plan. This lets you control what you do in class but saves you time on admin work. To get started, use the following prompt:
I will show you my notes. These notes are for a TEFL lesson for [age and level of students]. Please turn the notes into a full lesson plan. Including timings and stage aims. Output in a table format.
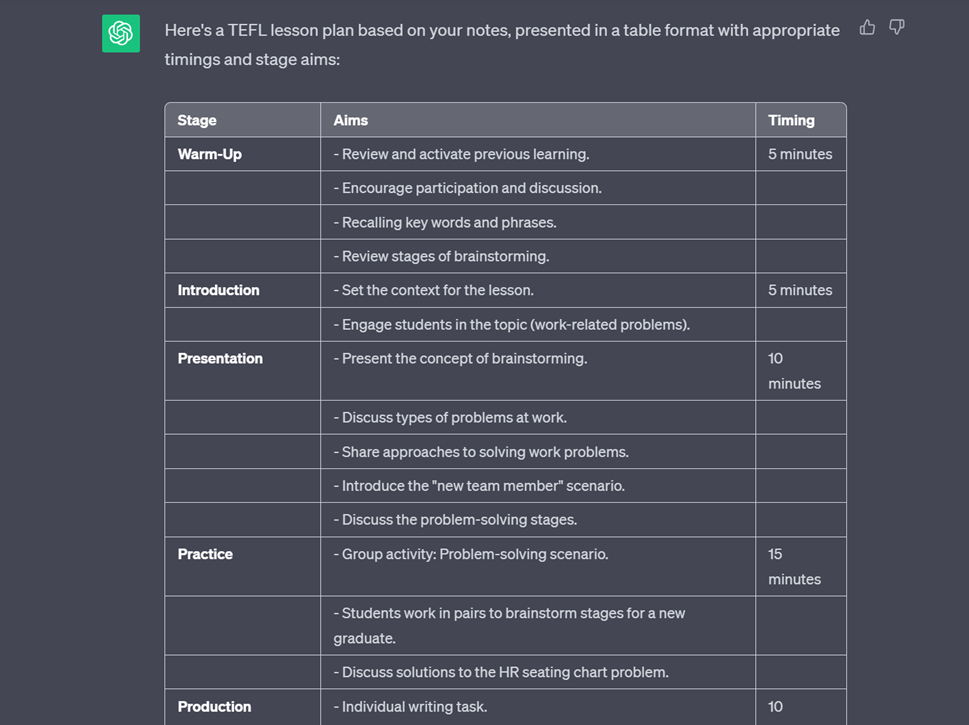
Above is an example of output from Chat GPT3.5

Above is an example of output from Bard.
Remember to read the content before submitting it to your supervisor. AI models are good at using language creatively, but they’re not mind readers. You may need to make some adjustments to the content, especially if an administrator is likely to read it.
Limitations
AI isn’t perfect. Before using AI in the planning process, you should know some of its limitations.
- Grading language. At the moment, most AI models struggle to grade language. That means that examples of target language in lesson plans might be too hard for your students. Make sure that you check the language in the plan is appropriate for your learners.
- Biased planning. AI models are trained on data. If that data is biased, then the plans created by the AI will also be biased. For example, if the AI has been trained on plans which use PPP, the plans the AI produces are likely to use PPP. That does not mean PPP is the best way to stage a lesson.
- Adaption. AI has never met your students and has never taught a class. The more information you give the AI about your students and your teaching style, the better the plans should be. However, there is no substitute for your teaching experience and knowledge of your students. Adapt your lesson plans to fit your context.
- Logic. AI makes mistakes with logic. You may find the timings in the lesson plans do not add up to the length of your class. The activities might not match the stages they are under. Check whatever the AI produces to make sure it makes sense.
Conclusions
AI is a great tool for lesson planning. It can generate ideas, write lesson aims, give suggestions for activities and most importantly, save time. However, AI is not a replacement for your creativity, judgment, and expertise. Whatever you produce using AI, remember to review and adapt the content. Ask yourself, how could I make this more appropriate for my students? Would this work with my teaching style? And are you sure this will help your students?
AI for Language Teaching Course
You can now gain your very own AI credential through our newly launched AI for Langauge Teaching course. This 30 hour course was created specifically for TEFL/TESOL teachers, with the goal of saving you precious time, while safe-guarding quality in the process. Learn more about the course here.
AI for Language Teaching
Master AI, save time and transform your TESOL teaching with our 30-hour course.



